A Guide to Resolving Network Connection Troubles
In the digital age, where our lives are intricately woven into the vast web of the internet, a seamless and reliable network connection is paramount. The frustrating dance of “No Internet Access,” “Limited Connectivity,” or simply a weak signal can leave us momentarily stranded in the online wilderness. In this comprehensive guide, we venture into the heart of Windows network connectivity issues. From elusive Wi-Fi troubles to Ethernet hiccups, we explore the common culprits, network troubleshooting techniques, and the expert strategies that will empower you to regain your digital lifeline.
What’s Covered in This Guide
- Eliminating the Obvious.
- How to use the Network Repair Tool.
- Obtaining an IP Address automatically.
- Choosing a Different DNS.
- How to Flush your DNS.
- How to reset your Network assigned IP address.
- How to reset any Firewall configurations including rules and policies.
- How to reset IPv4 Protocol configurations.
- How to reset IPv6 Protocol configurations.
- How to reset the Winsock Layered Service Providers.
Once these steps have been completed you should hopefully be back online surfing the web without any issue.
Basic Steps
These first steps may seem obvious, and you have likely tried them already, but we need to cover them as they are the most common problem with network connectivity issues.
- Unplug your router for 30 seconds then plug it back in and make sure it’s turned on.
- Reboot your PC.
- Try accessing the internet from a different device connected to your network.
- If you can’t access your network with any other device, then you should contact your broadband supplier.
So now we have eliminated the obvious causes, we can move on to the technical stuff, but don’t worry I will make it as simple a process as possible.
Using the Network Repair Tool
The Network Repair Tool is the best place to start, it will suggest troubleshooters with recommend actions if problems are detected.
Right-click the Wi-Fi icon (bottom right) and select Open Network & Internet settings.
If your version of Windows doesn’t display the Network and Sharing Center here, you can find it in the Control Panel settings, Control Panel > Network and Internet > Network and Sharing Center.
Select Network and Sharing Center

Select Troubleshoot problems.
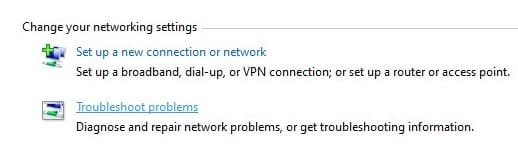
If there are any detected problems, there will be appropriate troubleshooters recommended.

If that resolved the problem, great! Reboot your system and check everything is still ok. If you’re still having a problem, continue on to the next step.
Obtaining IP Automatically and Manually Selecting your DNS
Your system should already be setup to obtain an IP automatically, but it’s worth checking regardless. Changing your DNS (Domain Name Service) can also resolve many issues. Here we are going to use the Google DNS service, which is very reliable.
Right-click the Wi-Fi icon (bottom right) and select Open Network & Internet settings.
If your version of Windows doesn’t display the Network and Sharing Center here, you can find it in the Control Panel settings, Control Panel > Network and Internet > Network and Sharing Center.

Select Change Adapter options.
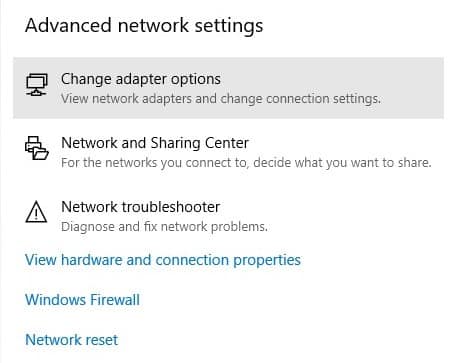
Right-click your Wi-Fi adapter and select properties.
Highlight Internet Protocol Version 4(TCP/IPv4) by clicking it, and then select properties.
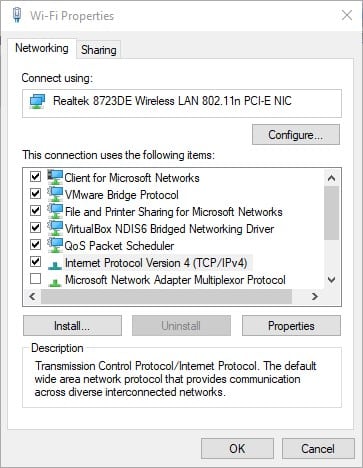
Make sure the Obtain an IP address automatically box is checked.
Now check the box Use the following DNS server addresses:
Then in the Preferred DNS server: add the following:
8.8.8.8In the Alternate DNS server: add the following:
8.8.1.1Just like in the image below.

Select OK and reboot your system. Test you network connection, if the problem persists, then continue to the next step.
How to Flush the DNS Cache
Flushing the DNS records will not cause any network connection issues, but it may help to fix them.
Click the Windows Start button (bottom left) and type cmd in the search bar, now choose Run as administrator. If your account doesn’t have administrator level privileges you must log in with the account that does, the rest of these steps will all require administrator level access.

To some the Command Prompt window can seem an intimidating place when used to Windows, but don’t panic, if you enter the commands incorrectly you will just see an error message and no harm can be done.
With the Command Prompt open enter the following command:
ipconfig /flushdnsThis will flush all DNS records. The DNS cache may have out of date records, or may even have become corrupted, this is easily resolved by flushing the DNS cache.
Now try to connect to the online service you were having trouble with. Take note after flushing the DNS, web pages or services may be slow to load the first time you access them as your system is performing a full DNS lookup, which can add a delay to the loading of any content. Flushing the DNS will not speed up your connection, but it can make sites and services load faster.
Once the process is complete, test you network connection, if the problem persists, then continue to the next step.
Releasing and Renewing your Network IP
Now we can try releasing your network assigned IP and requesting a new one from your router.
Your network assigned IP will look something similar to 192.168.0.10 this address is assigned by your router, and each network attached device in your home will have a unique address, so traffic can be directed to the correct device.
If you rebooted the system or closed the command prompt, click the Windows Start button (bottom left) and type cmd in the search bar, now choose Run as administrator.
To release your network assigned IP, enter the following command into the Command Prompt:
ipconfig /releaseNow your IP has been released back to the router you will need to request a new network assigned IP, don’t be surprised if you are assigned the same address, just know that it’s still newly assigned. Take note, you will have no connection to the network until you request a new address from the router.
To request your new IP, enter the following command into the Command Prompt:
ipconfig /renewBe patient the renew process might take a minute or two.
To view your newly assigned IP, enter the following command:
ipconfigNow, try and access the online services again. If the problem persists, continue to the next step.
Resetting NetBIOS
To clear the NetBIOS name cache, enter the following command:
nbstat /RTo clear NetBIOS names registered with WINS server (Windows Internet Name Service) and re-register them, enter the following command:
nbstat /RRReboot your system to complete the process. If the problem persists, continue to the next step.
Resetting your Network Adapter
Now we can try something a little more advanced. This is typically for more experienced users, but it really can’t do any harm if this is just your Personal Computer.
I don’t recommend you try this on enterprise level computers or servers without having the knowledge to troubleshoot any issues that may arise after. If you proceed you do so at your own risk.
Make sure to save any open work before you continue.
Click the Windows Start button (bottom left) and type cmd in the search bar, now choose Run as administrator.
First, we will reset the firewall settings with the following command:
netsh advfirewall resetThis will reset any custom firewall rules and configured security policies, to the default security rules and policy configurations.
Now in the Command Prompt, enter the following command:
netsh int ip resetThis resets any configured IPv4 protocol settings. A reset is required for the default settings to activate.
If you rebooted the system or closed the command prompt, click the Windows Start button (bottom left) and type cmd in the search bar, now choose Run as administrator.
Now in the Command Prompt, enter the following command:
netsh int ipv6 resetThis resets any configured IPv6 protocol settings. A reset is required for the default settings to activate.
If you rebooted the system or closed the command prompt, click the Windows Start button (bottom left) and type cmd in the search bar, now choose Run as administrator.
Now in the Command Prompt type the following Command:
netsh winsock resetThis will reset the Winsock list to a clean state.
Now reboot your system and the internet should be working.
If Everything has Failed
If your internet is still failing, it could be possible your NIC (network interface card) is at fault, and you should look into replacing it or seeking further advice from your local computer repair shop.
Conclusion
From eliminating the obvious to utilizing powerful tools and resetting critical configurations, you’ve acquired a toolkit that empowers you to be the master of your network’s destiny. Those cryptic “No Internet Access” messages and elusive connectivity glitches hopefully no longer hold power over your digital life.
Remember, as technology evolves, so do the challenges it presents. But with your newfound knowledge, you’re equipped to navigate the ever-changing landscape of network troubleshooting. Your Windows device is no longer a source of perplexity; it’s a resilient bridge to the digital world.
Happy Computing Folks!
If you want to keep up to date with our latest posts, or you just want to say hi, why not follow us on Twitter/X
If you want to show your support, why not browse through our Products page and see if there is anything you need. Meganano receives a small profit from each sale made via our affiliate links.




