
Welcome to our guide on intermediate Linux terminal commands! If you’ve got the basics down, you’re ready to take the next step. Here, we’ll explore handy tools for files, users, and more.
Linux Text Editing Tools
Ready to get better with Linux text editing tools? These commands make editing files a breeze:
nano: A simple choice for quick edits. For example, typenano /etc/hosts.vimorvi: A solid editor for tweaks. Start withvim script.sh, then pressi.emacs: A flexible option among Linux text editing tools. Useemacs config.conf &to run it.
Pro Tip: Try vim shortcuts like hjkl to speed up your work with these tools!
Linux File Permissions Basics
Want to learn Linux file permissions basics? Here’s how these commands help you control access:
chmod: Change access easily. For instance,chmod -R u+x scripts/makes files runnable.chown: Set a file’s owner. Trychown user1 file.txtas part of Linux file permissions basics.chgrp: Switch group access. Usechgrp developers project/.
Also, try chmod 755 file.sh for quick permission setups.

Monitor Linux Processes
Need to monitor Linux processes? These tools keep you on top of what’s running:
ps: See active processes. Typeps auxfor details.toporhtop: Watch live stats. Runhtopto monitor Linux processes clearly.kill: Stop a process. For example,kill -9 1234ends it fast.

Tip: Use ps aux | grep name for quick process checks.
Package Management with Intermediate Commands
Updating your system? Here’s what to use for package handling:
Debian/Ubuntu
apt-get: Add software. Trysudo apt-get install nginx.dpkg: Handle.debfiles. Usedpkg -i package.deb.
Red Hat/Fedora
yum: Install packages. Runsudo yum install httpd.rpm: Use.rpmfiles. Typerpm -ivh package.rpm.
Pro Tip: Refresh Debian with apt-get update && apt-get upgrade.
File Searching Commands
Need to find files fast? Try these search tools:
find: Search by name. Tryfind / -name "*.log".locate: Quick searches. Runlocate config.confaftersudo updatedb.
Text Manipulation Tools
Working with text? These commands are great for the job:
grep: Find patterns. For example,grep -r "error" /var/log/.sed: Edit text fast. Usesed 's/old/new/g' file.txt.awk: Pull out data. Tryawk '{print $1}' file.txt.
Combo: cat access.log | grep "404" | awk '{print $7}' grabs 404 links.
Archiving and Compression
Packing files? Check out these compression tools:
tar: Group files. Usetar -cvf archive.tar dir/.gzip: Shrink files. Rungzip file.txt.zip/unzip: Make.zipfiles. Tryzip archive.zip *.txt.
One-Liner: tar -czvf archive.tar.gz dir/ does both.
Linux Network Troubleshooting
Need help with Linux network troubleshooting? These commands get you connected:
ip: Check network info. Typeip addr show.ping: Test a connection. Useping -c 10 google.com.ssh: Log in remotely with Linux network troubleshooting. Tryssh user@192.168.1.10.scp: Move files securely. Runscp file.txt user@remote:/path/.

Linux User Account Setup
Starting with Linux user account setup? These commands make it simple:
useradd: Add a user. Usesudo useradd -m -s /bin/bash obiwan.passwd: Set a password. Trysudo passwd obiwan.usermod: Update a user with Linux user account setup. For example,sudo usermod -aG sudo obiwan.userdel: Remove a user. Runsudo userdel -r obiwan.
Group Management
Sorting users into groups? Here’s how to do it:
groupadd: Make a group. Usesudo groupadd jedi.gpasswd: Add users to groups. Trysudo gpasswd -a obiwan jedi.groups: See user groups. Rungroups obiwan.
Password Policies
Keeping accounts secure with Linux user account setup? Try this:
chage: Set password rules. For instance,sudo chage -M 60 obiwan.
File Transfer Commands
Moving files around? Give these a go:
wget: Grab files online. Usewget https://example.com/file.zip.curl: Download stuff. Runcurl -O https://example.com/file.txt.rsync: Sync files. Tryrsync -av dir/ remote:/backup/.
System Information
Curious about your system? Check these out:
uname: See system details. Useuname -a.df: Check disk space. Rundf -h.free: View memory. Tryfree -m.
More Useful Tricks
Want to boost your skills? For example:
rm -r dir1: Delete a folder and its contents.cat file1 file2 > file3: Mix two files into one.grep -n "word" file1: Find words with line numbers.whoami: See your username.
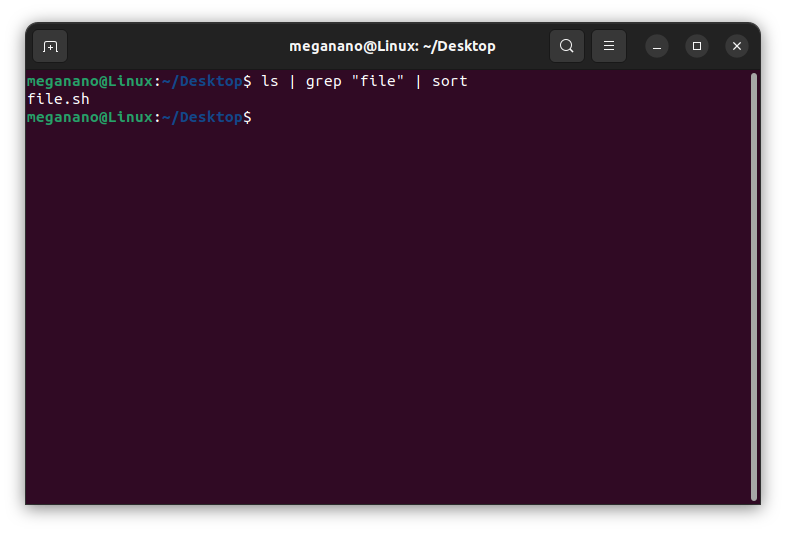
Power Move: Chain commands like ls | grep "file" | sort.
Great Job!
If you made it to the end and you understand everything, we have covered today then you’re fast becoming a Linux master, well done!
If you want to keep up to date with our latest posts, or you just want to say hi, why not follow us on Twitter/X
If you want to show your support, why not browse through our Products page and see if there is anything you need. Meganano receives a small profit from each sale made via our affiliate links.




